Theory of Switching regulators
Nguyên lý Bộ biến đổi xung
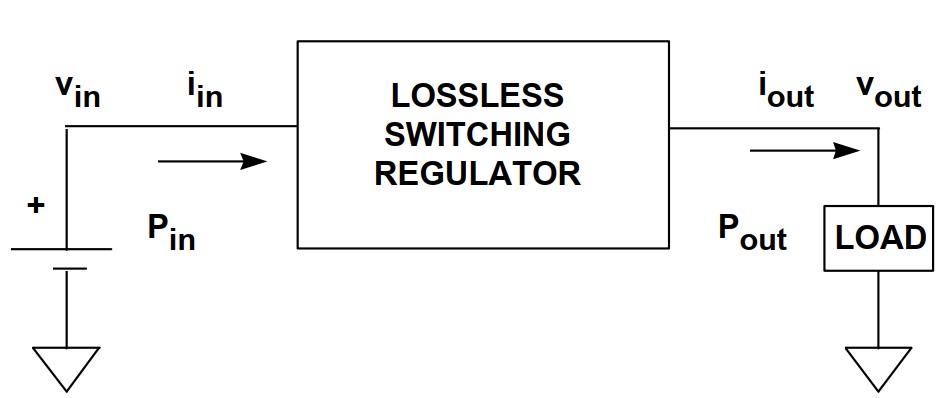
Virtually all of today's electronic systems require some form of power conversion. The trend toward lower power, portable equipment has driven the technology and the requirement for converting power efficiently. Switchmode power converters, often referred to simply as "switchers", offer a versatile way of achieving this goal. Modern IC switching regulators are small, flexible, and allow either step-up (boost) or step-down (buck) operation.
When switcher functions are integrated and include a switch which is part of the basic power converter topology, these ICs are called “switching regulators”. When no switches are included in the IC, but the signal for driving an external switch is provided, it is called a “switching regulator controller”. Sometimes - usually for higher power levels - the control is not entirely integrated, but other functions to enhance the flexibility of the IC are included instead. In this case the device might be called a “controller” of sorts - perhaps a “feedback controller” if it just generates
the feedback signal to the switch modulator. It is important to know what you are getting in your controller, and to know if your switching regulator is really a regulator or is it just the controller function.
Also, like switchmode power conversion, linear power conversion and charge pump technology offer both regulators and controllers. So within the field of power conversion, the terms “regulator” and “controller” can have wide meaning.


 Tính toán quấn máy biến áp 1 pha tần số 50Hz
Tính toán quấn máy biến áp 1 pha tần số 50Hz 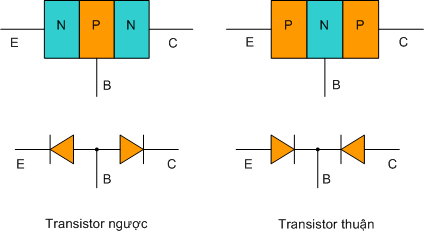 Cấu tạo, nguyên tắc hoạt động của Transitor
Cấu tạo, nguyên tắc hoạt động của Transitor  Nguyên lý và sử dụng nguồn xung hay bộ biến đổi nguồn DC-DC
Nguyên lý và sử dụng nguồn xung hay bộ biến đổi nguồn DC-DC  Làm LED trái tim với 8501
Làm LED trái tim với 8501  Ký hiệu, Hình dạng, kiểm tra, Xác định chân Transitor
Ký hiệu, Hình dạng, kiểm tra, Xác định chân Transitor 

